Command line support for Add-On system
In the new version of EPiServer 7.5 we have added a new feature to the Add-On system – command line operations support. The web interface is still the primary way to manage add-ons on a site, but now there is an alternative that can be used if the web interface is not available. It is implemented as a PowerShell Snap-In that is installed together with the installation of EPiServer 7.5. The Snap-In contains the following CmdLets:
Get-EPiAddOnConfiguration
This command returns technical details about the Add-On system configuration: public or protected modules locations, repositories folders etc.
Get-EPiAddOnFeeds
Returns a list of configured add-on feeds. By default the Add-On system has three feeds configured (EPiServer Add-Ons, EPiServer Beta and Third-Party Add-Ons)
Get-EPiAddOns
Returns a list of add-ons installed on the site or a list of add-ons that can be installed from a specified feed
Add-EPiAddOn
Installs an add-on from a specified feed or from a file
Remove-EPiAddOn
Uninstalls an add-on from the site.
Update-EPiAddOn
Updates an add-on on the site to specified version
Enable-EPiAddOn
Enables a previously disabled add-on on the site
Disable-EPiAddOn
Disables an add-on on the site. This is a new feature of EPiServer 7.5 – an add-on can be disabled, which means that it is not active and its code is not executed and its content is not available on the site, but it is still present in the list of installed add-ons, so user can easily enable it back, upgrade or delete and the add-ons data, if any, are preserved. Disabling might be particularly useful when solving issues related to add-ons compatibility. We also use it in the upgrade scenario.
You can find detailed description of all CmdLets in the documentation.
For developers these commands might be interesting for automation purposes or as tool for resolving issues related to add-ons. It might happen during development that an add-on installation make the site not accessible and there is no way to uninstall it from the sites web interface. Before there was not so many options, removing the add-on manually requires some knowledge of the Add-On system internals. Now there are two more options – disable or uninstall an add-on from the command line.
In order to be able to use the commands “EPiServer.Install.Packaging” Snap-In need to be added to the session. Run PowerShell command line tool (if you have 64-bit operating system, please use 32-bit PowerShell, here you can find how to do this) and type the following command:
Add-PSSnapin EPiServer.Install.Packaging.*
If nothing happened and you just returned back to the command prompt – it’s fine, it means that the Snap-In was just successfully loaded.
For starters we can try to list add-ons installed on a site (note that the site should be EPiServer 7.5):
Get-EPiAddOns –ApplicationPath C:\EPiServer\ExampleEPiServerSite
Command returns all installed add-ons and their properties. In order to simplify commands input it is recommended to save current site path in a variable and use the variable as ApplicationPath parameter value. Also in order to reduce the noise we can pipe its output to the Select command:
$sitePath = “C:\EPiServer\ExampleEPiServerSite\wwwroot” Get-EPiAddOns –ApplicationPath $sitePath | Select Id, Version
What if we want to do the same for a site that has EPiServer 7? Use ApiPath parameter:
$apiPath = “C:\Program Files (x86)\EPiServer\Framework\7.5.394.2\Install\Tools” Get-EPiAddOns –ApplicationPath $sitePath –ApiPath $apiPath | Select Id, Version
Note: current version of CmdLets loads required Add-On system assemblies in AppDomain of the current PowerShell session, so it is better to not execute commands against different versions of EPiServer sites in the same command line session.
We can also filter output from the command:
Get-EPiAddOns –ApplicationPath $sitePath | Where {-not $_.IsSystemPackage} | Select Id, Version
We can disable Add-On like this:
Disable-EPiAddOn –ApplicationPath $sitePath –Id MyAddOn
Or uninstall it:
Remove-EPiAddOn –ApplicationPath $sitePath –Id MyAddOn
Note: Please use Remove command with caution. Since this command doesn’t call BeforeUninstall method, the add-on that is going to be uninstalled does not have a chance to clean up after itself properly.
We can pipe output from one command to another. For example we can disable all add-ons, which can be disabled:
Get-EPiAddOns –ApplicationPath $sitePath | Where {$_.CanBeDisabled} | %{Disable-EPiAddOn –ApplicationPath $sitePath –Id $_.Id } | Select Id, Version, IsDisabled
Then we can enable them back:
Get-EPiAddOns –ApplicationPath $sitePath | Where {$_.IsDisabled} | %{Enable-EPiAddOn –ApplicationPath $sitePath –Id $_.Id } | Select Id, Version, IsDisabled
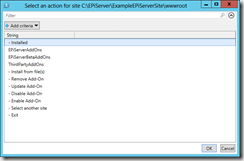
If you don’t really fond of remembering all those commands you can use this small script that provides a basic interface for all add-on operations available from the command line. It allows you to select the site interactively from the same dialog that is used in the Deployment Center and then provides a menu interface for operations with selected site add-ons:

Comments