Optimizely DXP Health Checks and Creating Custom Checks
Introduction
In this blog I'm going to be talking through the standard Azure health checking system and how the DXP is setup to operate health checks. Then I'm going to explain how to easily create your own health checks to allow monitoring parts of the system so that unhealthy instances can be easily removed.
Thanks as well to Valdis and Mark Hall who helped me get this point!
Azure Heath Checks
Within Azure there is a feature called a heath check https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/app-service/monitor-instances-health-check?tabs=dotnet which is designed to allow you to provide information about the state of your application and if it's healthy or unhealthy. This allows the load balancer to deterimine if there are any unhealthy instances and remove them so that the overall health of the application can recover quickly as shown.
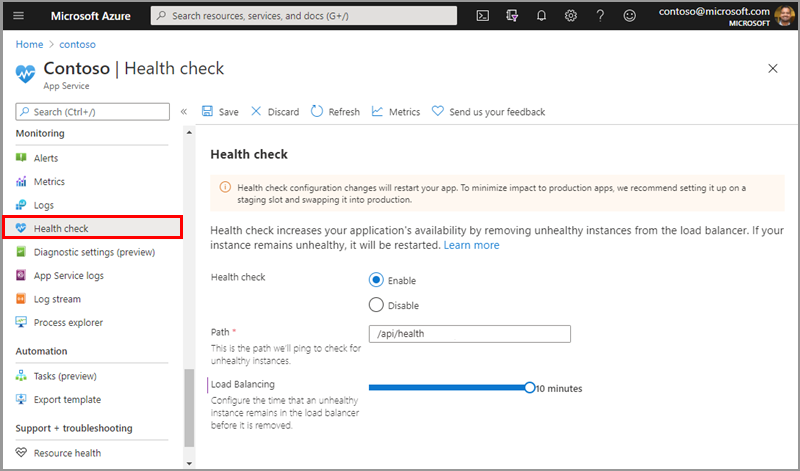
Optimizely DXP Health Checks
Optimizely has a specific setup of heathcheck that's set up in the middleware and configured as standard in the Azure WebApps hosted by the DXP.
The following is setup as standard within the DXP WebApps
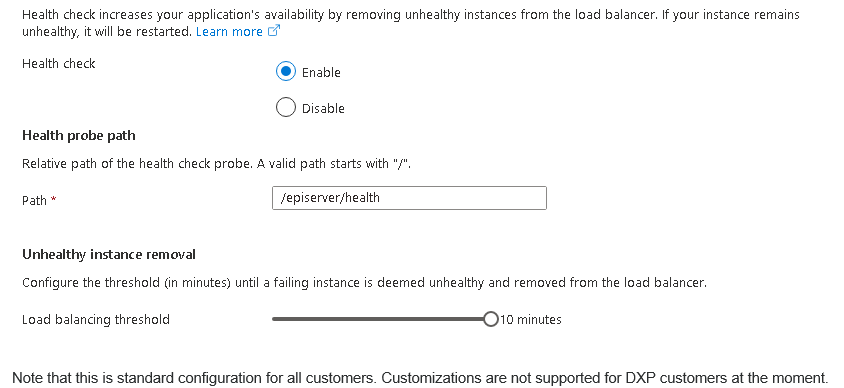
As you can see there is a specific route that has been configured for Optimizely health checks. So how does this all work?
Within a typical DXP startup.cs you'll have a call to
.AddCmsCloudPlatformSupport(_configuration)And if we decomiple this code we see a specific bit of code that sets up this health check configuration
public static IServiceCollection AddCloudPlatformHealthCheck(this IServiceCollection services)
{
services.TryAddEnumerable(ServiceDescriptor.Singleton<IEndpointRoutingExtension, CloudPlatformHealthCheckEndpointRoutingExtension>());
services.AddHealthChecks().AddCmsHealthCheck(tags: ((IEnumerable<string>) new string[2]
{
"episerver",
"content-api"
})).AddCmsWarmupHealthCheck(tags: ((IEnumerable<string>) new string[1]
{
"warmup"
}));
return services;
}This code does a few things
- Sets up the routing for the /episerver/health
- Adds the CmsHeathCheck which loads the class CmsHealthCheck (This checks some information about the schema / database version)
- Adds the AddCmsWarmupHealthCheck which does checks for a warm up using pings defined in the environments WEBSITE_HEALTHCHECK_MAXPINGFAILURES
So this does a few things to allow Optimizely to report if the Instance is healthy or unhealthy but what about if we want to add to this?
Adding Custom Checks
This is actually really easy based upon what we've seen here
- Create a class that inherits IHealthCheck
- Create an extension method to register is part of the IHealthChecksBuilder
- Add it to the startup.cs using the AddHealthChecks() extension
Create a class that inherits IHealthCheck
My class will specifically force an unhealthy state so we can test it in postman but in your own code obviously do a check for whatever you want and return Healthy if it's all okay!
public class CustomHealthCheck : IHealthCheck
{
public Task<HealthCheckResult> CheckHealthAsync(HealthCheckContext context, CancellationToken cancellationToken = new CancellationToken())
{
return Task.FromResult<HealthCheckResult>(HealthCheckResult.Unhealthy("Test failed"));
}
}Create an extension method to register is part of the IHealthChecksBuilder
public static class CustomHeathCheckExtensions
{
public static IHealthChecksBuilder AddCustomHealthCheck(
this IHealthChecksBuilder builder,
string name = "custom-health-check",
HealthStatus status = HealthStatus.Unhealthy,
IEnumerable<string> tags = null)
{
return builder.AddCheck<CustomHealthCheck>(name, new HealthStatus?(status), tags);
}
}Add it to the startup.cs using the AddHealthChecks() extension
Add it on the end of the services expressions as shown here for Alloy
services
.AddCmsCloudPlatformSupport(_configuration)
.AddCmsAspNetIdentity<ApplicationUser>()
.AddCms()
.AddAlloy()
.AddAdminUserRegistration()
.AddEmbeddedLocalization<Startup>()
.AddHealthChecks()
.AddCustomHealthCheck();Testing
A quick note on this is that adding .AddCmsCloudPlatformSupport(_configuration) locally will cause an error so a way to test this locally is to comment this out and manually register the .AddCloudPlatformHealthCheck() as shown below
services
//.AddCmsCloudPlatformSupport(_configuration)
.AddCmsAspNetIdentity<ApplicationUser>()
.AddCms()
.AddAlloy()
.AddAdminUserRegistration()
.AddEmbeddedLocalization<Startup>()
.AddCloudPlatformHealthCheck()
.AddHealthChecks()
.AddCustomHealthCheck();Then with this is place you'll get an unhealthy response back, as shown in postman when hitting that endpoint
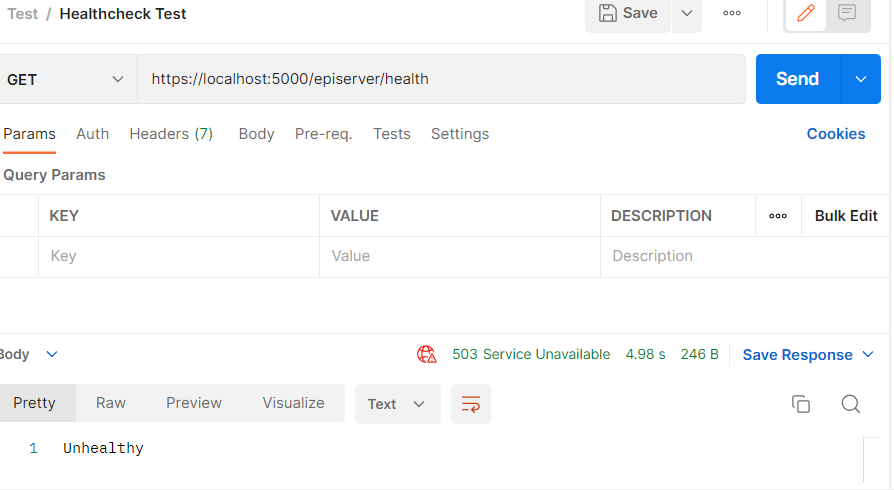
Conclusion
Hopefully this helps explain exactly how the heath checking system is working in a bit more detail and gives you some ideas should you want to be able to have greater control is telling the load balancer when your instance is unhealthy :-)

Excellent!
Thanks Scott.
Great article thanks Scott
Thanks Scott! I could make it work but wondering about best basic criteria to determinate healthiness. Since I don't have any external integration or special service running in my solution, I have in mind just to try to load StartPage with contentLoader. If that success, it means App and DB are running. Any other better idea?
David, the default out of the most platform health checks are probably fine then, I'd only suggest implementing health checks if there's custom scenarioes that you're having issues with such as say caching problems or integration and you need to force a removal/restarted of an affected instance from the LB