Episerver CMS is based on Microsoft technology and uses Internet Information Services (IIS) as web server, and .NET Framework and ASP.NET as a web development platform. Episerver uses the SQL Server relational database. On top of that, Episerver has a framework API used by all products in the Episerver platform.
In this topic
- The .NET framework
- System overview
- Customized solution
- Database
- Web server
- Development environment
- Developing for the cloud
The .NET framework
Episerver is based on the .NET/ASP.NET framework, providing the following advantages:
- Easier for developers to quickly implement solutions using Visual Studio extensions.
- Flexible integration with other systems and platforms using Web services.
- Improves performance using the integrated cache functions in .NET.
In Episerver .NET is implemented in accordance with Microsoft guidelines. Since .NET is a language-independent architecture, developers have a wide choice of development methods for their solutions. Episerver CMS is written in C#, but developers are free to use other programming languages such as VB.NET or J#. Episerver CMS development in .NET is fully object-oriented. See the Microsoft .NET documentation.
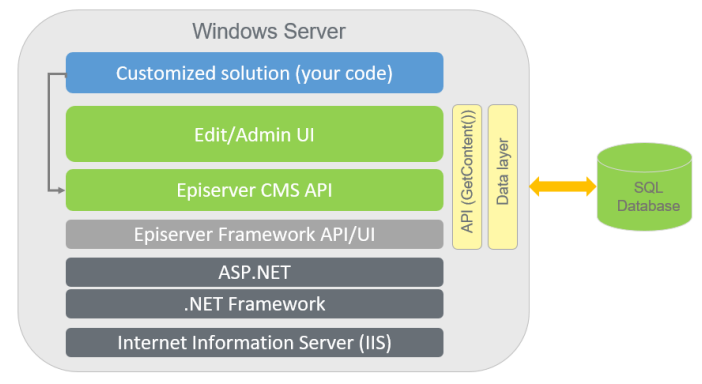
System overview
The base Episerver CMS Framework provides built-in editorial and administrative functions like version management, content preview, approval workflows, multi-language support, and access rights. Data is stored in an SQL database. The customized solution is built on top of this platform. Episerver can run as an on-premise installation, or in the cloud. See Episerver system requirements.
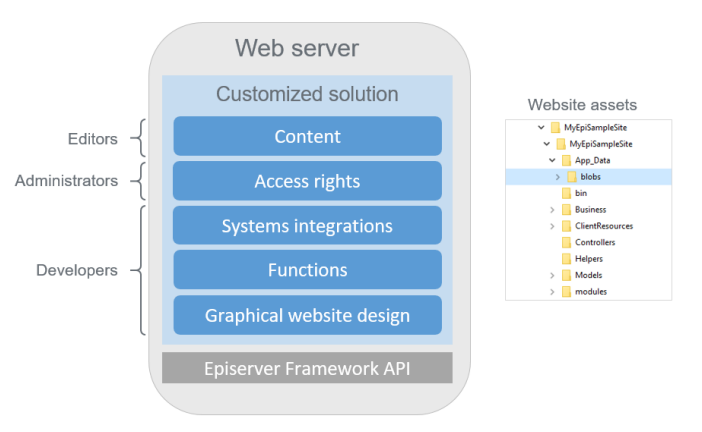
Customized solution
A customized solution typically contains these parts:
- Graphical profile for the site as style sheets (CSS format). These contain predefined colors and fonts used on the site. Responsive design is often applied to support multi-channel display.
- Functions to support content creation, for example specific page or block types.
- Systems integrations as required for the site, for example connection to an article database.
- Access rights configured for users and user groups, to control access to the content structure and publishing. May involve integration with external membership providers.
- Content created by editors, and stored in the database.
- Assets such as images and documents used on the site.
Database
Episerver uses Microsoft SQL Server to store content and other information created in the system. All database editions including SQL Azure are supported. A database with the Episerver schema is automatically created when creating new sites from the Visual Studio integration. Each version of the database schema targets a specific version of Episerver.
Web server
On-premise Episerver sites in production use Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS), which is a flexible, general-purpose web server that runs on Windows operating systems to serve requested HTML pages or files. When developing locally, you can use IIS Express which is included with Visual Studio, and then move to the full IIS when ready to go live. See Deployment.
Development environment
Episerver solutions are conveniently developed using Windows, SQL Server, and Visual Studio from Microsoft. Episerver also provides a set of Visual Studio extension templates, to speed up website development.
It is recommended to use MVC rather than Web Forms, when building Episerver websites with ASP.NET. The main advantages are better control of generated HTML, better testability and code reuse, and better complexity handling. See the ASP.NET MVC documentation.
Developing for the cloud
An Episerver solution can be hosted in the cloud or on-premise. Cloud-based solutions are a cost-efficient way to manage websites, as these will dynamically scale out and in again depending on traffic volume, and the cost is based on usage and number of running instances. You can manage your cloud-based solutions yourself, or use Episerver DXP.
Related topics
- Microsoft .NET documentation
- Episerver system requirements
- Episerver Customer-Centric Digital Experience Platform
- Episerver Visual Studio extension
- ASP.NET MVC documentation
Next topic in Learning path
Last updated: Oct 19, 2021
